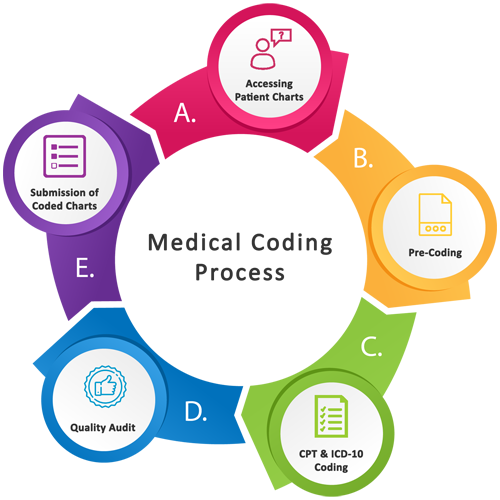
Medical coding is a crucial process in the healthcare industry that involves converting medical procedures, diagnoses, and services into standardized alphanumeric codes. These codes are used for various purposes, including billing, insurance claims, medical record-keeping, and statistical analysis. Proper medical coding ensures accurate and consistent documentation of patient encounters, facilitates communication among healthcare providers, and enables the smooth functioning of healthcare systems.
There are two main coding systems used in medical coding:
1. International Classification of Diseases (ICD): This system is developed and maintained by the World Health Organization (WHO). It assigns alphanumeric codes to medical diagnoses and is currently in its 10th revision (ICD-10).
2. Current Procedural Terminology (CPT): The CPT coding system is maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA). It uses numeric codes to represent medical procedures, treatments, and services provided to patients.
Let’s briefly discuss the two types of codes:
CPT(Current Procedure Terminology)codes:
These are the codes which denote the procedures performed in the outpatient or inpatient setting. The American Medical Association (AMA) maintains these codes. CPT codes are updated every year.They are generally 5-digit codes divided into 3 categories:
1. The Category I codes are further divided into 6 classes: Evaluation and Management (E/M), Anesthesia, Surgery, Radiology, Pathology and Laboratory, and Medicine.
2.The Category II codes describe the laboratory tests and radiology procedures.
3.The Category III codes depict the new upcoming medical treatments or procedures.
ICD (International Classification of Diseases)codes:
The World Health Organization (WHO) is responsible for maintaining and revising the ICD system. The most widely used version of ICD is the ICD-10, which is the tenth revision.ICD coding is used in various healthcare-related activities, including:
1.Medical Coding: ICD codes are used by medical coders to classify diagnoses and medical conditions.
2.Epidemiology and Public Health: ICD codes are essential for analyzing disease patterns, tracking the occurrence of specific health conditions, and studying population health trends.
2.Clinical Documentation and Research: ICD codes are used in medical records and research studies to standardize and categorize health information.
2. Medical Coding Training

Medical coding training is essential for individuals who want to pursue a career as a medical coder. It provides the necessary knowledge and skills to accurately assign medical codes to diagnoses, procedures, and services. Proper training ensures that medical coders can perform their duties effectively and efficiently, helping healthcare providers with billing, insurance claims, and medical record-keeping. Through are online training classes you can connect to us anytime, anywhere. We provide with live sessions, chat facilitates to solve your queries, and training videos on different aspects of coding.We have regular webinars (2 to 3 hours) for all the students. These webinars not only focus on lectures by our trained professionals, but also on discussions with the students. The partaking student can also submit his queries.
Our classroom trainings are given by professional coders. We have classes the entire week and the weekends. we prepares you for certification program by providing you with manuals and taking test every week. before every class a refreshment session of 20 minutes is conducted in the form of a quiz. our classrooms are well-equipped with modern day technology, which would further enhance your learning experience.
Both our online and classroom training programs focus on:
- • Preparing you for exam with advanced technology
- • 100% job oriented programs
- • Professional approach to pass the exam
- • Tips to focus on useful information
- • Guidelines
- • Easy tips for time management during the exam
- • Mock question papers
3. Medical Coding Syllabus
Certificate Exams and Syllabus
The health care system is changing at a fast pace. You need to be updated as the employers also want certified professionals who can adapt to this rapid changing environment. There are several medical coding certification exams offered by reputable organizations. The most widely recognized certifications in medical coding include:
Certified Professional Coder (Cpc)
The CPC certification is one of the most sought-after credentials in the medical coding field. It focuses on outpatient coding and covers various topics related to CPT, ICD-10-CM, HCPCS Level II coding, medical terminology, anatomy, and healthcare regulations. The exam consists of multiple-choice questions and requires a passing score to earn the CPC designation.
The details of the exam are:
Exam fee: $530
No. of attempts: 2
AAPC membership: $175
Exam format: 150 Questions – Multiple Choice (open book)
Exam duration: 5 hours 40 minutes
Mode of exam: Written exam
CEUs to be submitted: 18 per year
The CPC exam has vast syllabus that may include:
ICD-10 CM guidelines, Digestive system, Urinary system and male genital system, Female reproductive system, Maternity care and delivery, Endocrine system, Nervous system, Anesthesia, Radiology, Laboratory and pathology, Evaluation and management services, Medicine.
Certified Outpatient Coder (COC)
The COC certification is specifically targeted at individuals who specialize in outpatient facility coding. The exam assesses knowledge of outpatient coding guidelines, CPT, HCPCS Level II, and ICD-10-CM coding.
The details of the exam are:
Exam fee: $530
No. of attempts: 2
Exam format: 150 Questions – Multiple Choice (open book)
Exam duration: 5 hours 40 minutes
Mode of exam: Written exam
CEUs to be submitted: 10 per year
The COC exam has vast syllabus that may include:
Outpatient hospital facilities and departments, Business in facility, Compliance in outpatient facility, Documentation and coding standards, Anatomy and physiology, ICD-10 CM guidelines, Musculoskeletal system, Respiratory system, Cardiovascular system, Digestive system, Urinary system and male genital system, Female reproductive system, Maternity care and delivery, Endocrine system, Nervous system, Anesthesia, Radiology, Laboratory and pathology.
Certified Inpatient Coder (CIC)
CIC is inpatient coding. The reimbursement in an inpatient setting is entirely based on the procedures used during the treatment. The exam is sponsored by the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC).
The details of the exam are:
Exam fee: $530
No. of attempts: 2
Exam format: 60 Questions – Multiple Choice (open book); 10 inpatient cases
Exam duration: 5 hours 40 minutes
Mode of exam: Written exam
CEUs to be submitted: 10 per year
The CIC exam has vast syllabus that may include:
Inpatient facilities and related hospital departments, Inpatient documentation and coding, Inpatient diagnosis coding- general guidelines, Inpatient diagnosis coding – chapter specific guidelines, ICD-10 CM guidelines, Application of ICD-10-CM codes, CMS and inpatient prospective payment system, Outpatient perspective payment system, Regulatory and payer requirement, Business in the facility, Anatomy and physiology, Medicine.
Certified Professional Medical Auditor (CPMA)
CPMA is auditing the medical records. The aim of the audit is to improve and re-evaluate the codes applied in the medical records. Also, CPMA is important to prevent any fraud, waste or abuse, and to prevent overpayment. The exam is sponsored by the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC).
The details of the exam are:
Exam fee: $530
Attempts: 2
Exam format: 150 Questions – Multiple Choice (open book)
Exam duration: 5 hours 40 minutes
Mode of exam: Written exam
CEUs to be submitted: 16 per year
The CPMA exam has vast syllabus that may include:
Fraud, waste and abuse, Federal false claim act, Anti-kickback law, Stark law, Exclusion statute, HIPAA Privacy Regulations, Types and components of medical records, Accreditation standards, Evaluation and Management o Anesthesia, Surgery, Radiology, Pathology and Laboratory, Auditing process, Statistical sampling, utilization review, RAT-STATs, Validation of audit results.
Certified Coding Specialist (CCS)
The CCS certification is designed for professionals with inpatient coding expertise. The exam assesses candidates' knowledge of ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS coding systems, as well as other topics like pharmacology, reimbursement methodologies, and healthcare regulations.
The details of the exam are:
Exam fee: $399
No. of attempts: 2
Exam format: 79 Questions – Multiple Choice (open book); 8 medical situations
Exam duration: 4 hours
Mode of exam: Written exam
The CCS exam has vast syllabus that may include:
Health Information Documentation Diagnosis and Procedure Coding Regulatory Guidelines and Reporting Requirements for Inpatient setting Regulatory Guidelines and Reporting Requirements for Outpatient setting Information and communication technologies Privacy, confidentiality, legal and ethical issues Compliance
4. Medical Coding FAQs
1.What are the advantages of medical coding?
A good career opportunity, which will last for a long time period as a provider will never be free of patients.
2.Is Medical coding easy?
Yes, The difficulty of medical coding can vary depending on several factors, including a person's background, prior knowledge of medical terminology and anatomy, attention to detail, and the complexity of the coding scenarios encountered.
3.What skills should I have to work as a coder?
You should be confident and deliver quality work within the given deadlines.
4.What training/s do I need to undergo for medical coding?
Knowledge of anatomy and physiology, and medical terms is very important. Look for a training program that trains you in:
1. Medical terminology
2. medical coding software
3. basic health care insurance cycle
4. policies and guidelines
5.Where do medical coders work?
Medical coders may work in hospital setting, ambulatory centers, ambulatory centers, emergency rooms and insurance companies. They may also work online from home.
6.What other work/job can a medical coder do?
A professional certified medical coder can work as a bookkeeper or in payroll in an organization. There are many other roles depending on your experience and education.
